Tension Headache Treatment
Tension headaches occur when neck and scalp muscles become tense or contract, is continuous in nature, like a band around a head, pressure and squeezing in character and will last for few hours to few days.
- The muscle contractions can be a response to stress, depression, head injury, or anxiety. They may occur at any age, but are most common in adults and older teens.
- Tension headaches typically don't cause nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light. They do cause a steady ache, rather than a throbbing one, and tend to affect both sides of the head. Tension headaches may be chronic, occurring often, or every day.
Tension Headache Symptoms
Muscle contractions in the head and neck are considered a major factor in the development of a tension headache. Some people get tension headaches in response to stressful events or hectic days.
These are common symptoms of a tension headache:
- a:-Slow onset of the headache.
- b:-Head usually hurts on both sides.
- c:-Pain is dull or feels like a band or vice around the head.
- d:-Pain may involve the back part of the head or neck
- e:-Pain is usually mild to moderate, but not severe
Symptoms of a Headache
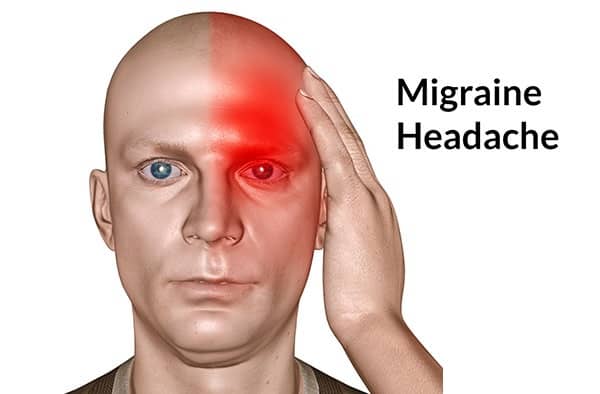
Migraine Headache
WHAT IS A MIGRAINE?
Migraine is a neurological disorder, characterized by intense or severe pain and headache lasting at least four hours to several days. Migraine is often accompanied with other symptoms in addition to head pain; it tends to worsen by and interfere with physical activity.
Migraine headaches will typically affect only one side of the head. However, it is possible to affect both sides of the head. Migraine pain can be moderate to severe. Some people experience migraines so severe they seek medical care at an emergency room.
Approach Considerations:-
Migraine treatment involves acute (abortive) and preventive (prophylactic) therapy. Patients with frequent attacks usually require both. Measures directed toward reducing migraine triggers are also generally advisable.
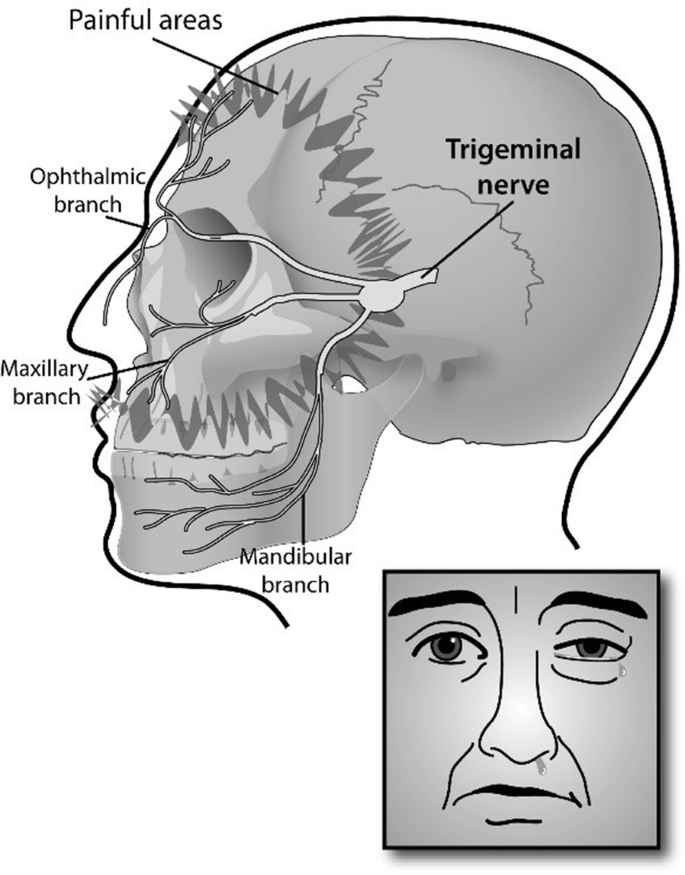
CLUSTER HEADACHES
Is a severe headache, on one side ofthe head with recurrence on fixedtime intervals.
Cluster headaches, which occur in cyclical patterns or cluster periods, are one of the most painful types of headache. A cluster headache commonly awakens you in the middle of the night with intense pain in or around one eye on one side of your head
- 1-Swollen ordrooping eye.
- 2-Smaller pupil in the eye.
- 3-Eye redness or watering.
- 4-Runny or congestednose
- 5-Red, warm face
- 6-Sweating
SYMPTOMS:-
- 1-Cigarette smoke
- 2-Alcohol
- 3-Disruptions in your circadian rhythm, like sleep deprivation and jet lag etc.
SYMPTOMS:-
Cluster Headache Treatment:-
- 1:-Measures to Abort the acute episode with medicine such as sumatriptan, and other treatments, including oxygen therapy, can help reduce the incidence and severity of attacks.
- 2:-Preventive medicine can be given by the treating doctor as required
- 3:-Avoid taking Alcohol
 For More Info
For More Info